Last Updated: Dec. 14, 2025
Editor’s Note (Dec. 10, 2025): Added internal link to new guide on post-mining economics.
Bitcoin mining is the process that validates transactions on the Bitcoin network and releases new BTC into circulation. Miners compete to solve cryptographic puzzles using specialized hardware, and the first to find a valid solution earns the block reward: currently 3.125 BTC (worth approximately $320,000 at December 2025 prices) plus transaction fees from that block.
Mining serves two critical functions. First, it secures the network by making it computationally expensive to attack or manipulate transaction history. Second, it controls the supply of new Bitcoin entering circulation, following a predetermined schedule that will cap the total supply at 21 million BTC.
How Bitcoin Mining Works
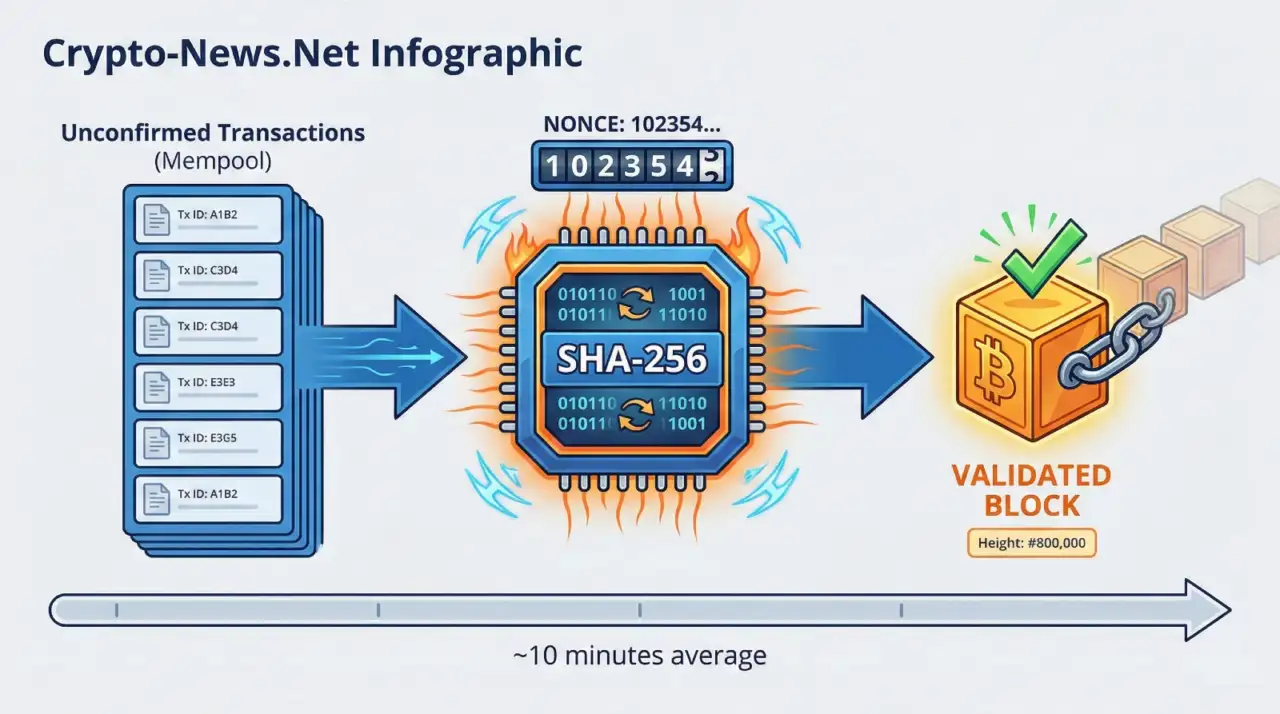
Every Bitcoin transaction must be verified before it becomes permanent. When you send BTC to someone, that transaction enters a waiting area called the mempool. Miners collect these pending transactions, bundle them into a block, and compete to add that block to the blockchain.
The competition centers on finding a valid hash. A hash is a fixed-length string of characters produced by running data through a cryptographic function called SHA-256. Bitcoin’s protocol requires the hash to start with a certain number of zeros, and the only way to find one that qualifies is through brute-force guessing.
Miners adjust a variable called a nonce (number used once) to change the hash output. They cycle through billions of nonce values per second until someone finds a hash that meets the network’s difficulty target. The first miner to succeed broadcasts their solution to the network. Other nodes verify it, and if valid, the block is added to the blockchain.
This entire process repeats approximately every 10 minutes. The network difficulty adjusts every 2,016 blocks (roughly two weeks) to maintain this 10-minute average, regardless of how much computing power joins or leaves the network.
The Mining Process Step by Step
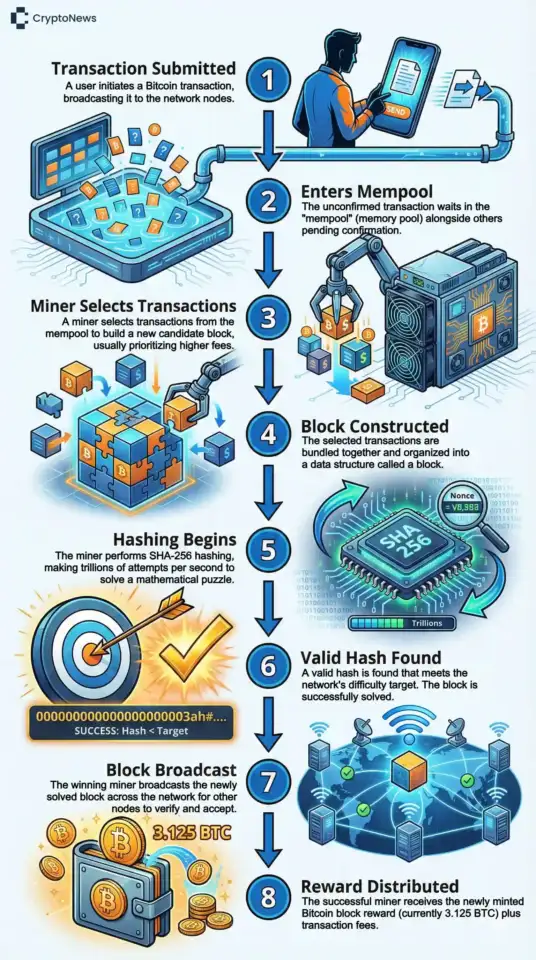
Here is what happens each time a new block is mined:
- Transactions accumulate in the mempool, waiting for confirmation
- Miners select transactions to include in a new block, typically prioritizing those with higher fees
- Each miner constructs a block header containing the previous block’s hash, a timestamp, and a nonce
- Mining hardware runs SHA-256 calculations, testing billions of nonce values per second
- When a miner finds a hash below the target threshold, they broadcast the block to the network
- Other nodes verify the block’s validity by checking the hash and confirming all transactions follow protocol rules
- Once accepted, the block joins the blockchain permanently
- The winning miner receives 3.125 BTC plus all transaction fees from that block
Bitcoin Mining Hardware
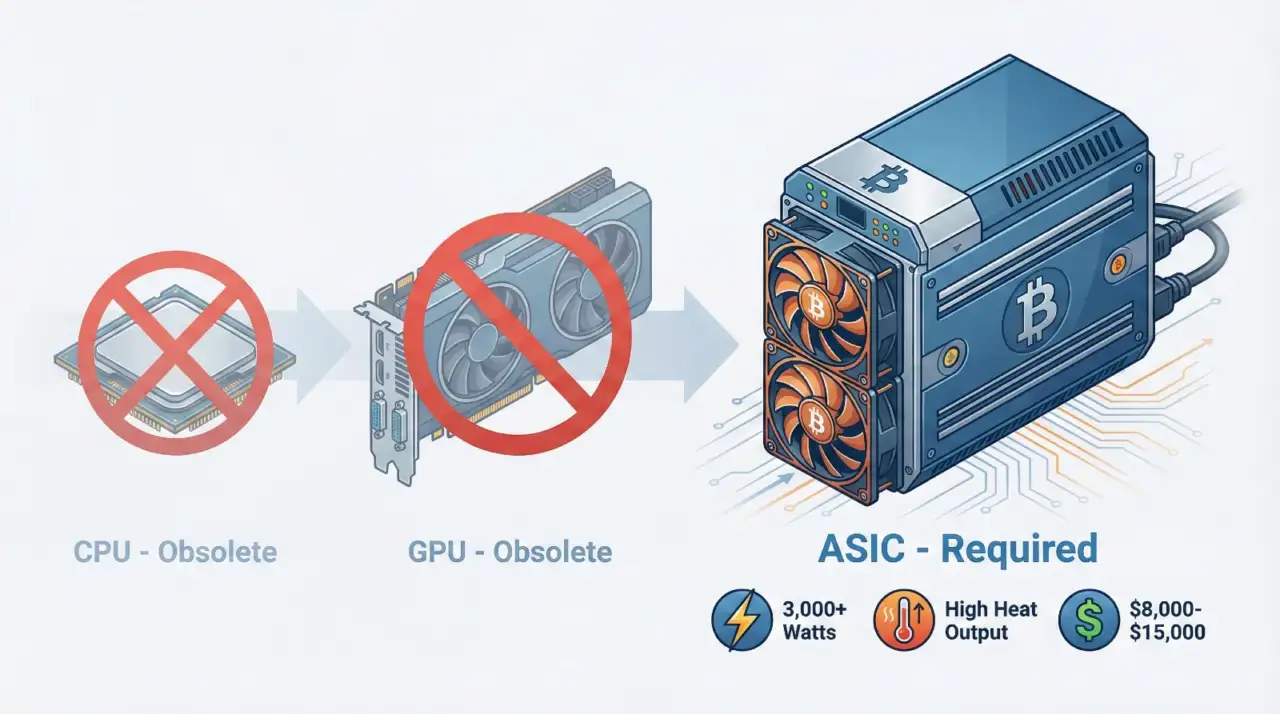
In Bitcoin’s early years, anyone could mine using a regular computer’s CPU. By 2010, miners discovered that graphics cards (GPUs) could perform hash calculations much faster. Today, neither option is viable.
Modern Bitcoin mining requires Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs), which are chips designed exclusively for SHA-256 hashing. Current models include the Bitmain Antminer S21 XP and the MicroBT Whatsminer M60S. These machines cost between $8,000 and $15,000 and deliver hash rates measured in hundreds of terahashes per second.
The economics are straightforward but unforgiving. An ASIC that costs $10,000 and runs 24/7 will consume significant electricity. Unless you have access to power at $0.05 per kilowatt-hour or less, profitability becomes difficult. Most individual miners cannot compete with industrial operations that negotiate bulk electricity rates and deploy thousands of machines.
Mining Pools: How Miners Work Together
Solo mining is essentially a lottery. With the current network hashrate exceeding 800 EH/s, a single ASIC has almost no chance of finding a block independently. The expected time between solo-mined blocks could stretch into decades.
Mining pools solve this problem by combining the hashpower of thousands of participants. When the pool finds a block, the reward is distributed among members based on their contributed work.
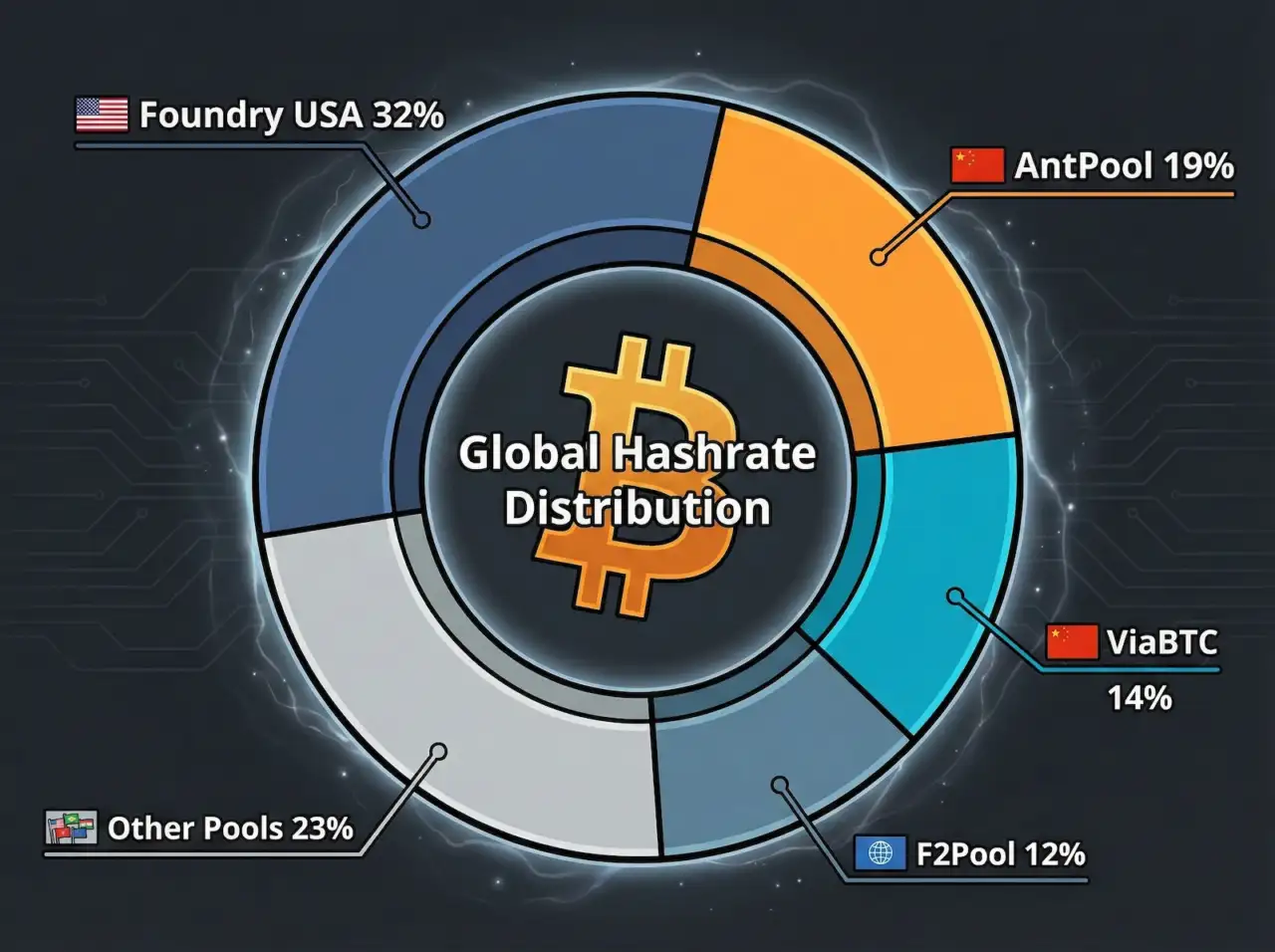
According to Hashrate Index data, the largest pools by market share are:
- Foundry USA: approximately 30-35% of network hashrate
- AntPool: approximately 17-21%
- ViaBTC: approximately 13-14%
- F2Pool: approximately 10-11%
Together, Foundry and AntPool control over 50% of Bitcoin’s mining power. This concentration raises decentralization concerns, though pool participants can switch pools at any time, providing some check on pool operator behavior.
Pools use different payout models. Pay-Per-Share (PPS) offers predictable income based on submitted work, regardless of whether the pool finds blocks. Full Pay-Per-Share (FPPS) adds estimated transaction fees to the payout. Pay-Per-Last-N-Shares (PPLNS) ties rewards directly to blocks found, creating more variance but potentially higher returns during lucky streaks.
Is Bitcoin Mining Profitable in 2025?

Profitability depends on four variables: hardware cost, electricity price, network difficulty, and Bitcoin’s market price.
The current mining difficulty stands at approximately 149 trillion, meaning miners must generate an astronomical number of hashes to find a valid block. This figure has climbed steadily as more hashpower joins the network and newer, more efficient machines come online.
The April 2024 halving cut block rewards from 6.25 to 3.125 BTC. Miners who were marginally profitable before the halving faced immediate pressure. Those with older equipment or expensive electricity either upgraded, relocated, or shut down.
For a rough calculation: a modern ASIC producing 200 TH/s at 3,000 watts, running on $0.08/kWh electricity, might generate $15-20 per day in Bitcoin at current prices and difficulty. Subtract the $7-8 daily electricity cost, and the margin is thin. Factor in cooling, maintenance, and the $10,000+ hardware cost, and breakeven stretches beyond two years.
Industrial miners with access to $0.03-0.05/kWh power and thousands of machines operate on different math entirely. Scale, efficiency, and power contracts determine who survives each halving cycle.
Bitcoin Mining’s Energy Consumption
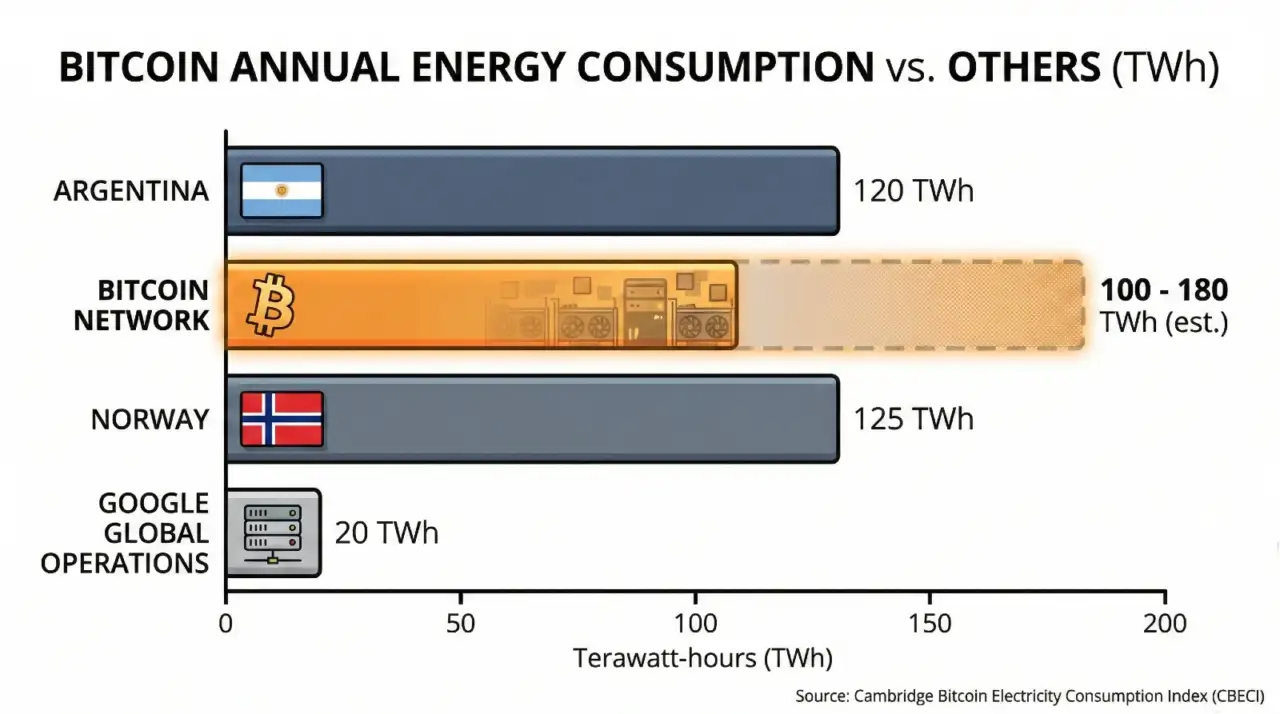
Bitcoin mining consumes substantial electricity. The Cambridge Bitcoin Electricity Consumption Index estimates annual consumption between 100-180 TWh, depending on methodology and assumptions about hardware efficiency.
For context, the U.S. Energy Information Administration notes this exceeds the total electricity consumption of many countries. Critics argue this energy use is wasteful, particularly when much of it historically came from fossil fuels.
Defenders counter that mining increasingly taps renewable or stranded energy sources. Hydroelectric power in regions with seasonal surplus, flared natural gas at oil drilling sites, and curtailed wind or solar generation all represent energy that would otherwise go unused. Some mining operations have co-located with renewable projects specifically to provide demand flexibility.
The debate continues, but the trend toward efficiency is clear. Each generation of ASIC hardware delivers more hashes per watt, and miners gravitate toward the cheapest available power, which increasingly means renewables.
Where Bitcoin Mining Happens
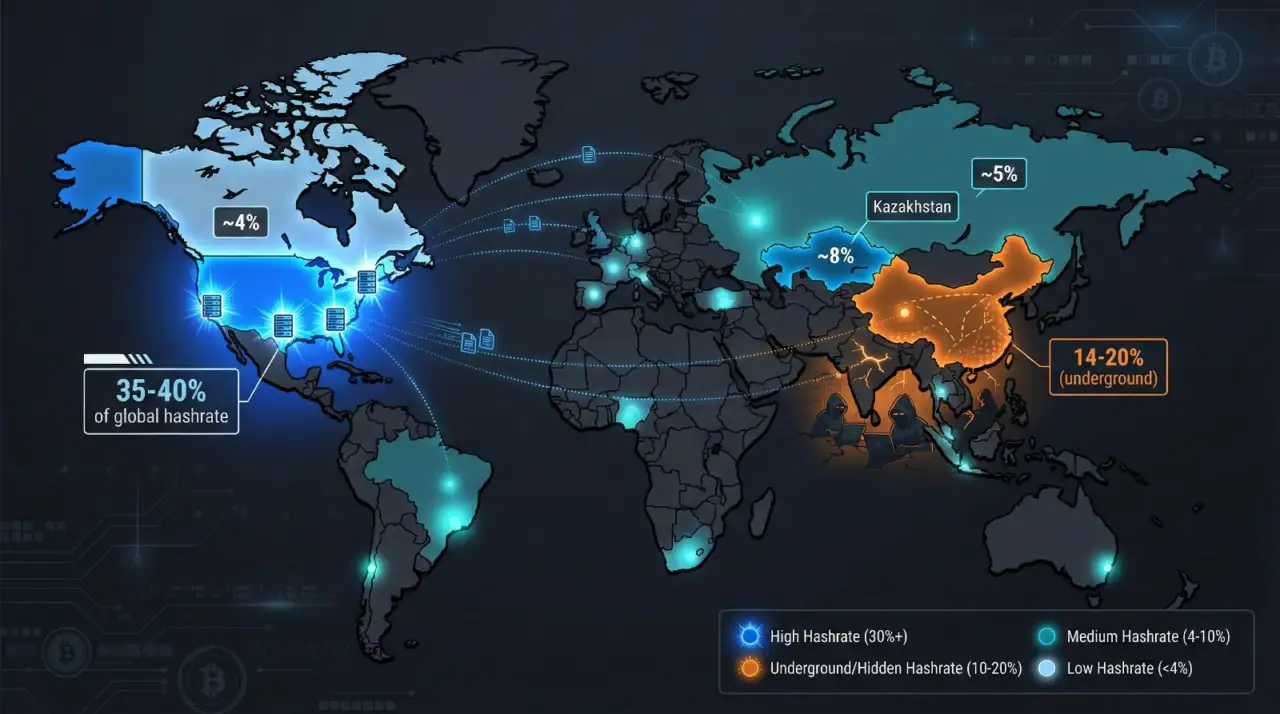
Bitcoin mining has undergone dramatic geographic shifts since 2021.
Before that year, China dominated with an estimated 65-75% of global hashrate. Cheap hydropower in Sichuan during wet season and coal-powered operations in Xinjiang and Inner Mongolia supported massive mining farms.
In September 2021, China’s National Development and Reform Commission officially banned cryptocurrency mining, citing financial risks and energy consumption concerns. Miners scrambled to relocate equipment to the United States, Kazakhstan, Russia, and other jurisdictions.
The United States emerged as the dominant mining hub, now hosting an estimated 35-40% of global hashrate. Texas, Georgia, and New York lead among states, attracted by deregulated energy markets, relatively friendly regulations, and existing data center infrastructure.
However, recent reports indicate China’s hashrate has quietly rebounded. Industry estimates suggest 14-20% of Bitcoin mining now occurs within China despite the official ban. Operations concentrate in energy-rich regions like Xinjiang and Sichuan, where excess electricity capacity and local economic pressures create incentives to look the other way. Mining equipment manufacturer Canaan reported that Chinese sales exceeded 50% of revenue in recent quarters.
Kazakhstan briefly became a major mining destination but has since imposed restrictions and raised electricity rates for miners. Russia hosts significant operations, though exact figures are difficult to verify.
Is Bitcoin Mining Legal?
The legal status of Bitcoin mining varies by jurisdiction.
In the United States, mining is legal at the federal level. State regulations differ: Texas actively courts miners with its deregulated grid, while New York imposed a moratorium on new proof-of-work mining operations using carbon-based power.
In China, mining remains officially banned since September 2021, though enforcement is uneven and underground operations persist.
Most European countries permit mining under existing regulatory frameworks, though energy costs often make it uneconomical. The European Union’s Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation focuses primarily on crypto service providers rather than miners.
Canada generally permits mining, with Quebec and Alberta hosting significant operations due to cheap hydroelectric and natural gas power.
Regulatory frameworks continue evolving. The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) provides guidance on virtual assets that influences national policies, though its focus is anti-money laundering rather than mining specifically.
For current legal status in specific jurisdictions, see our guide on whether Bitcoin is legal.
Bitcoin Halving and Mining Rewards
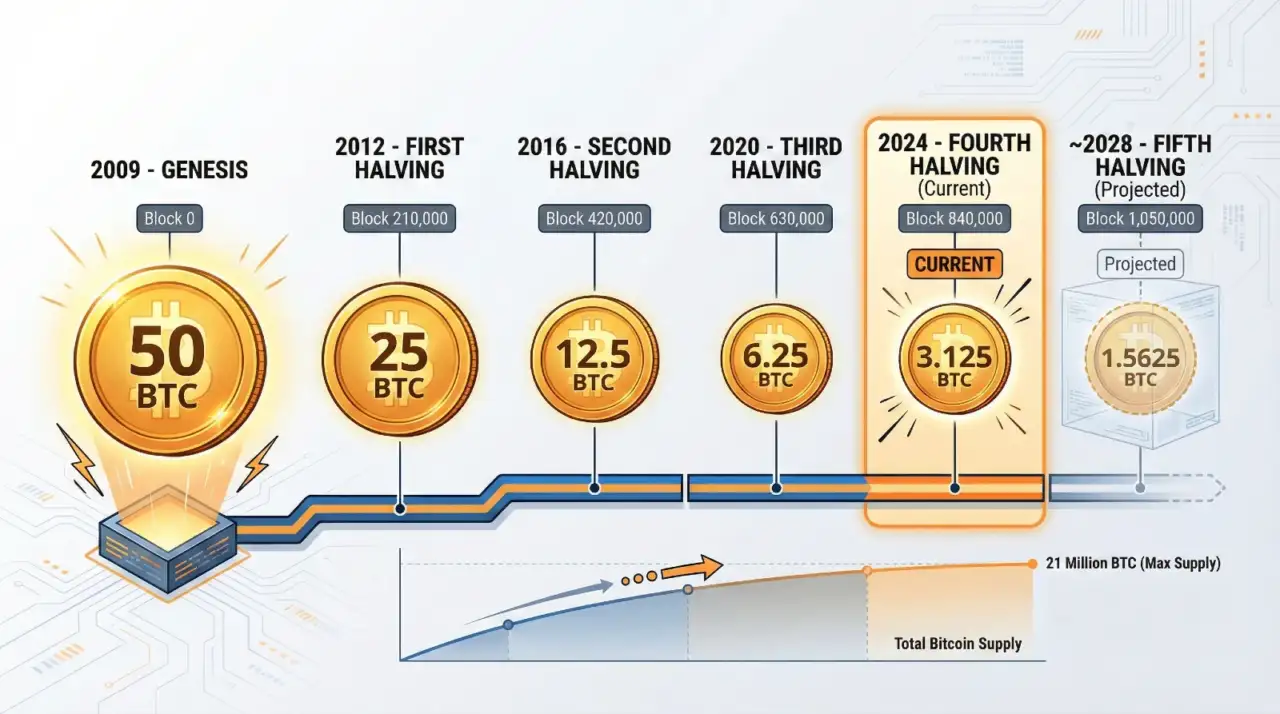
Bitcoin’s supply schedule is hard-coded into the protocol. Every 210,000 blocks (approximately four years), the block reward halves. This mechanism controls inflation and ensures the 21 million BTC cap is never exceeded.
The halving history shows the declining rewards:
- 2009: 50 BTC per block (Genesis)
- 2012: 25 BTC (first halving)
- 2016: 12.5 BTC
- 2020: 6.25 BTC
- 2024: 3.125 BTC (current)
- 2028: 1.5625 BTC (projected)
Each halving event forces miners to adapt. Those with high costs exit; those with efficient operations and cheap power absorb their hashrate. The network difficulty eventually adjusts downward if enough miners leave, restoring profitability for survivors.
Transaction fees will become increasingly important as block rewards diminish. Currently, fees constitute a small percentage of miner revenue, but by 2140 when all Bitcoin is mined, fees will be the only miner compensation.
Can You Mine Bitcoin at Home?
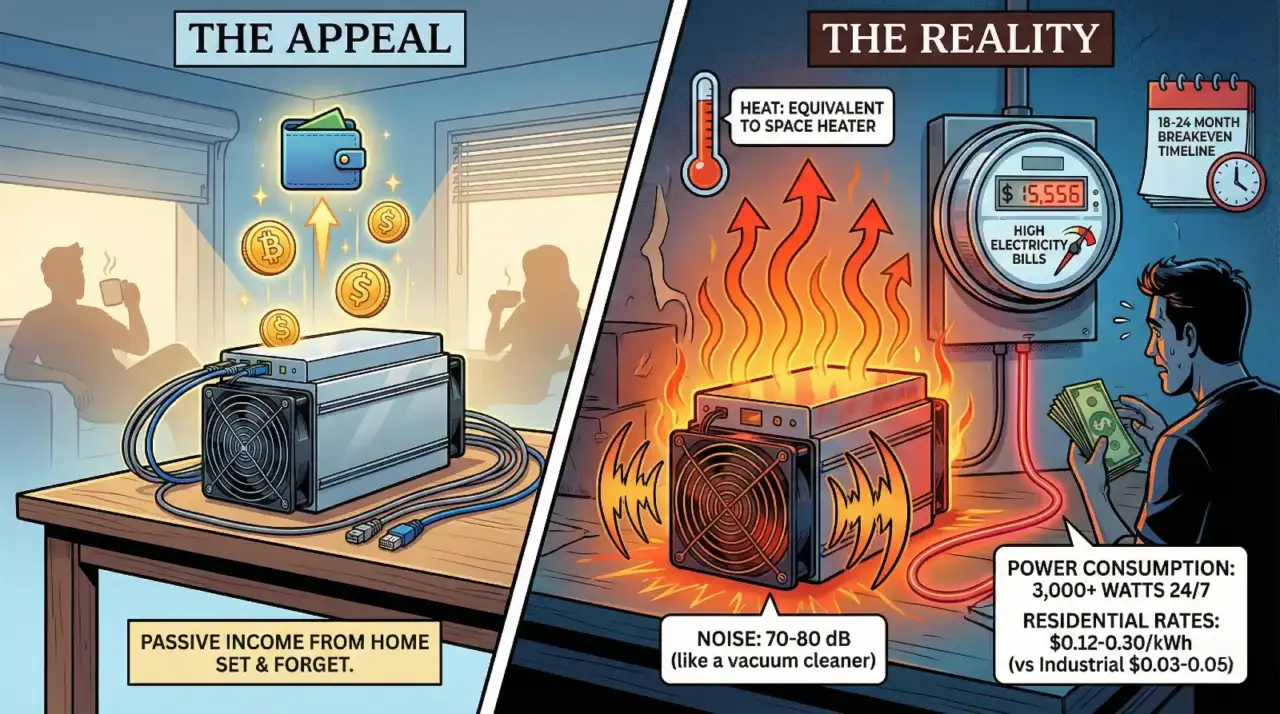
For most people, home Bitcoin mining is not economically viable. Residential electricity rates in the U.S. typically range from $0.10-0.20 per kWh, well above the threshold for profitability. A single ASIC running 24/7 can add $200-400 to monthly electricity bills while generating less value in Bitcoin.
However, an emerging trend reframes the economics: heat reclamation. ASICs convert nearly all consumed electricity into heat. Some homeowners and small businesses now use mining hardware as space heaters, treating any Bitcoin earned as a bonus rather than the primary purpose. Companies like Heatbit and others sell consumer devices designed around this concept.
Mining pools make participation technically accessible even with limited hardware, but the math rarely works at residential power rates. Those interested in acquiring Bitcoin will typically find buying it directly more cost-effective than mining.
The Future of Bitcoin Mining
Mining will continue evolving as technology advances and Bitcoin’s monetary policy plays out. Key trends to watch:
Hardware efficiency keeps improving. Each ASIC generation delivers more hashes per watt, pressuring operators of older equipment to upgrade or exit.
Energy sourcing is shifting toward renewables and stranded resources. Miners are among the most price-sensitive electricity consumers on Earth, and the cheapest electrons increasingly come from sources that traditional industry cannot easily access.
Geographic distribution remains fluid. Regulatory changes, energy prices, and political stability will continue reshuffling where mining occurs.
Institutional involvement is growing. Publicly traded mining companies, sovereign wealth funds, and traditional energy companies have entered the space, bringing capital and operational sophistication.
For the network, mining remains essential. It secures transactions, enforces Bitcoin’s monetary policy, and distributes new coins according to transparent rules. As long as Bitcoin has value, miners will compete to earn it.
Update History
Dec. 10, 2025: Added internal link to new guide on post-mining economics.
Dec. 5, 2025: Article completely rehauled and rewritten.
April 18, 2025: Original publication.
Sources: Cambridge Bitcoin Electricity Consumption Index, Blockchain.com, U.S. Energy Information Administration, Library of Congress, FATF, Hashrate Index